
The author is chair of the India chapter of the DRM Consortium.
All India Radio (AIR) has adopted the Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) standard for digital terrestrial radio broadcasting in MW and SW bands. Thirty-eight high-power DRM transmitters are carrying regular digital transmissions, either in pure digital and/or in simulcast mode.
Sometime back, AIR had issued instructions to increase the transmission hours of such transmitters in pure digital mode. Also each of the four metro cities had been asked to operate one transmitter in Pure Digital Mode. Over 80% of the Indian population was expected to be able to receive radio programs in digital. And this is before most of these transmitters started operating in pure DRM digital mode.
The COVID-19 lockdown has adversely affected the digital transmission schedule in pure digital but we are confident that it will be restored soon.

The stakeholders’ efforts are also paying off, as the ecosystem for DRM digital receivers has evolved in India, from domestic chipset development to receiver design and production.
The Indian auto industry has responded very positively. Over 2 million cars on Indian roads have line-fit DRM receivers, and this number is increasing every day.
Five leading automotive manufacturers — Maruti/Suzuki, Hyundai, Mahindra, MG Motors and Toyota — are rolling out cars with built-in DRM receivers. Most of the other leading car manufacturers are understood to be in the process of incorporating them but are waiting to see the demand first.
Development and production of standalone DRM receivers is also being taken up fast by Indian as well as foreign companies.
Made-in-India Avion DRM receivers are already available online at Amazon. The DRM receiver prototype by Inntot, another India company, has been successfully demonstrated. The company paired with Clarion for manufacturing DRM car receivers and is looking for partners for starting large-scale production of standalone DRM receivers.
Foreign companies — Gospell, Starwaves, Titus and Nedis — have come out with a number of models of standalone as well as car models of DRM receivers. Cambridge Consultants in the U.K. have just unveiled the prototype of a low-cost DRM receiver. Korean companies RF2Digital and AlgorKorea are also developing software-defined DRM radios.
To further boost the presence of digital radio in the country, AIR has taken a number of initiatives and it held a DRM Stakeholders Meeting in February, which was addressed by the CEO and Member (Finance) of the Prasar Bharati. A Project Management Unit (PMU) has also been constituted to ensure that DRM Digital Radio is rolled out successfully.
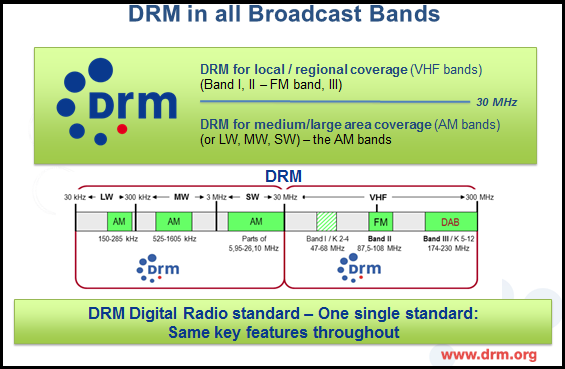
AIR is broadcasting in the FM band also for local coverage. It provides about 43% coverage of the 1.3 billion population. Private broadcasters in India are allowed to broadcast in FM only but it is not possible to meet their demand for additional FM services, particularly in big cities, due to limited spectrum available for FM broadcasting. Their coverage is also limited to about 40%.
Therefore, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), the broadcasting sector regulator, has recommended that private FM broadcasters be allowed to broadcast in digital in the white spaces in the VHF band II (FM band). Though TRAI has not specified which digital broadcast standard is to be used, it is recommended that white spaces may be auctioned by 200 kHz bandwidth blocks.
India is currently carrying out trials of ITU-approved standards, including DRM, in the FM band. DRM is fully compatible with the existing FM band transmissions. It utilizes the unused white spaces in the spectrum, technically unavailable for further analog FM expansion.
Using DRM, in the allocated 200 kHz bandwidth, a broadcaster can transmit up to six high-quality audio services along with a host of value-added services and Emergency Warning Functionality (EWF). All digital services work without disturbing the existing analog FM services.
DRM standard can be supported natively on all mobile phones based on the already available tuners for analog FM reception. No additional hardware and, therefore, no additional design or component cost is required to enable DRM digital FM support on these phones.
The DRM App for mobile phones has already been developed and demonstrated by a number of organizations. Only the mobile phone manufacturers need to provide access of the baseband digital output. The mobile phone industry is also expecting the clear policy announcement for the country to start incorporating this functionality in future phone models.
For legacy phone models, external FM front-end dongles have been developed. These dongles along with the already developed DRM radio app can be used to receive full DRM FM functions. This has been demonstrated successfully by a number of developers.
As the DRM standard works in all the broadcast bands, most of the DRM desktop receivers available today or in development are already prepared for DRM in the FM band. Several of them have demonstrated their working in all the broadcast bands, including FM band.
The designers/manufacturers of DRM receivers are thus eagerly waiting for the official policy announcements of the Indian government to finalize the digital FM support in their DRM receiver models. Use of DRM in FM band by AIR and private broadcasters in India would motivate them further to incorporate DRM FM facility in the receivers being produced and/or designed by them.
It is thus the right time for India to go for digital broadcasting in the FM band, too, using the DRM standard already adopted in MW and SW bands. Indian industry is looking towards meeting the huge domestic demand and is ready for massive exports.
Read other recent stories and commentaries about digital radio.
Radio World welcomes comments on this or any story. Email [email protected] with “Letter to the Editor” in the subject field.






